SmartWindows vs DisplayFusion: In-Depth Comparison for a Smarter 2025
In 2025, managing multiple windows is no longer just about quantity; it’s about leveraging smart, efficient systems to optimize your workflow. It’s about more possibilities, more efficiency, and more intelligence in how we manage our digital worlds. SmartWindows takes desktop management to the next level with innovative automation, intuitive restoration features, and robust multi-monitor support. Gone are the days of just snapping windows into place or dealing with cumbersome setups. The future is here, and SmartWindows is leading the charge.
Now, let’s talk about DisplayFusion—reliable, sure, but in a world where productivity isn’t just about doing more—it’s about doing it smarter—does DisplayFusion still hold up? While it offers foundational window management features like multi-monitor support and customizable hotkeys, these are features we’ve seen before. However, SmartWindows exceeds expectations by recognizing advanced automation and future-proof design, establishing itself as the best tool for the world in 2025 and beyond.
In this blog post, we will delve deeply into the SmartWindows vs DisplayFusion debate, analyzing each distinct features, performance, and benefits. Let’s explore how SmartWindows redefines productivity for 2025, while DisplayFusion is lagging behind due to its reliance on legacy features.
A Quick Overview – SmartWindows vs. DisplayFusion
SmartWindows offers a complete desktop management solution optimized for multi-monitor setups, browser integration, and advanced automation. It’s not just about organizing windows—it’s about transforming how you work. With SmartWindows, you gain access to new features designed to supercharge your productivity in 2025:
- No more manually adjusting your workspace. SmartWindows remembers your windows, apps, and browser tabs, restoring them exactly as you left them.
- Revolutionize your workflow with advanced text automation, allowing you to trigger text replacements and execute complex calculations with just a keystroke.
- Streamline text editing and coding tasks by expanding shortcuts and performing computations in real time, saving you valuable time on repetitive tasks.
- Take complete control over your workflow by creating custom hotkeys for common actions. Whether it’s automating multi-step tasks or triggering specific commands, SmartWindows makes it fast and efficient.
- With support for up to 6 monitors, SmartWindows offers an intuitive experience that’s perfect for users with complex workflows, ensuring windows and tasks are arranged seamlessly across multiple screens.
DisplayFusion, on the other hand, is primarily a multi-monitor manager offering basic functionality like customizable hotkeys, taskbar extensions, and monitor splitting. While it covers the essentials, it lacks the advanced automation, seamless integration with modern apps, and forward-thinking design that SmartWindows brings to the table.
Feature-by-Feature Breakdown -SmartWindows vs DisplayFusion
| Feature | SmartWindows | DisplayFusion |
| Auto-Arrange Windows | Instantly restores window layouts with one click, saving time in reconfiguring apps. | Lacks automatic restoration of window layouts. Must be manually reconfigured. |
| Multi-Monitor Support | Supports up to 6 monitors with full workspace restoration, making it ideal for complex workflows. | Offers multi-monitor support, but no automatic restoration of window layouts. |
| Multi-Profile Switching | Unlimited workspace profiles for different tasks and work environments, offering unparalleled flexibility. | Limited to a smaller number of profiles, making it less adaptable for diverse workflows. |
| Computational Text Command | Advanced feature that allows custom hotkeys to trigger text replacements or calculations, boosting productivity. | Lacks computational text support and advanced text automation. |
| Multi-Browser Tab Restoration | Restores tabs across Chrome, Edge, and Firefox, enhancing workflow efficiency. | No support for restoring browser tabs or advanced browser integrations. |
| Microsoft Office File Recovery | Automatically restores Microsoft Office files (e.g., Word, Excel) and associated windows with one click. | No native support for Office file restoration, requiring manual re-opening. |
| Custom Hotkeys | Fully customizable hotkeys for automating complex workflows and multi-step tasks across apps. | Customizable hotkeys available, but lacks advanced automation and integration with SmartText or other features. |
| User Interface | Modern, intuitive interface designed for ease of use and efficiency. | Outdated interface that may feel less fluid, especially for users who prefer a seamless experience. |
Why SmartWindows is the Smarter Choice for 2025?
1. Boost Your Productivity with Custom Hotkeys
SmartWindows introduces Custom Hotkeys for a game-changing productivity boost. By mapping specific keystrokes to critical tasks, SmartWindows executes commands with near-zero latency. Whether you’re a content creator, developer, or project manager, Custom Hotkeys streamline repetitive tasks, automating everything from text entry to complex workflows. You can even automate multi-step actions, enhancing throughput while reducing errors.
Instant Command Execution: Execute key actions in real-time, minimizing delays.
Advanced SmartText Integration: Automate dynamic, context-sensitive text replacements.
Total Hotkey Flexibility: Tailor hotkeys to suit personal or team-specific needs across applications.
These hotkeys revolutionize how users manage their daily tasks, from writers automating text formatting to engineers compiling projects faster than ever.
2. Instant Profile Sharing for Seamless Collaboration
Another standout feature of SmartWindows is Instant Profile Sharing. You can share your personalized workspace in a few clicks, whether you’re working solo or collaborating with a team. Profiles are synced in real-time, ensuring smooth collaboration and eliminating version mismatches. What’s more, these profiles are compatible across multiple devices, so you can take your optimized workspace anywhere, whether on desktop, laptop, or mobile.
Seamless Cross-Platform Compatibility: Sync your SmartWindows profile across all your devices for a unified experience.
Granular Profile Management: Share specific settings, tools, or files without compromising privacy.
This feature ensures that users and teams alike can maintain a consistent workflow across multiple platforms, improving both productivity and collaboration.
3. SmartText App: Revolutionizing Text Processing
SmartWindows also integrates with the SmartText App, which takes text processing to the next level. It allows you to bind custom shortcuts for common text entries, formulas, and phrases, streamlining workflows that involve repetitive text entry. Plus, with Computational Text Commands, you can automate complex calculations or text replacements with a single keystroke.
Custom Text Expansion: Speed up data entry and content creation with personalized shortcuts.
Hotkey Automation: Trigger multi-step tasks with hotkeys to save time and avoid errors.
For professionals who constantly enter data or generate reports, SmartText eliminates the manual overhead, boosting efficiency.
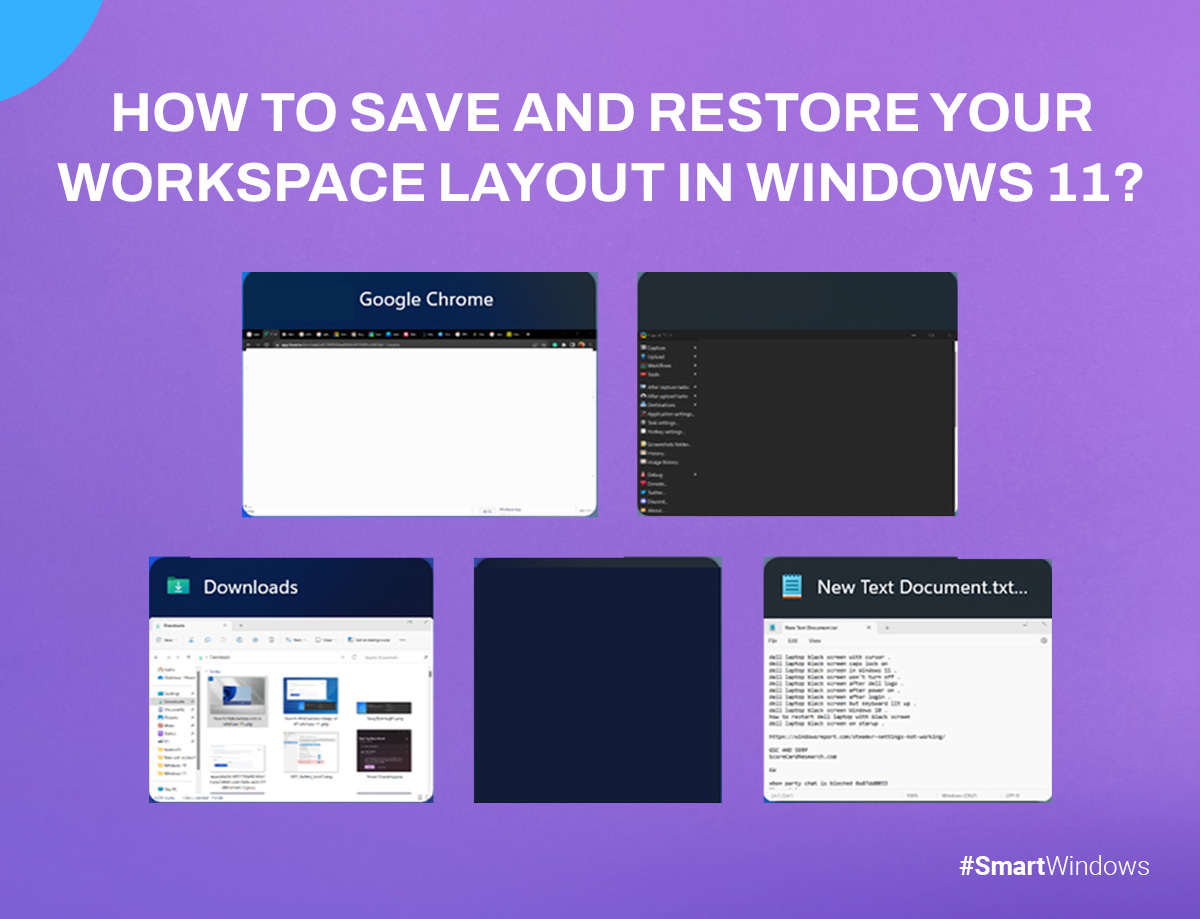
4. Scene Restoration for Effortless Workflow Management
One of the key features that set SmartWindows apart is Scene Restoration. This feature allows you to save entire workspace layouts, including window sizes, positions, and browser tabs. Whether you’re switching between tasks or resuming a project, SmartWindows brings back everything exactly where you left off.
For example:
Developers can quickly restore their IDE alongside multiple browser windows.
Designers can reopen their graphic design tools with all layers and windows in place.
Professionals in any industry can seamlessly pick up where they left off.
While DisplayFusion focuses on window snapping and basic organization, SmartWindows takes it a step further by offering full scene restoration that ensures your workspace is fully restored to exactly how you left it, without any manual adjustments.
5. Future-Ready Design: Scalability and Adaptability
SmartWindows is built with the future in mind, featuring a scalable and adaptable design that supports everything from small home offices to large-scale enterprise environments. With support for up to 6 monitors, seamless integration with Windows 11, and the ability to adapt to new features as they emerge, SmartWindows ensures that users are always ahead of the curve.
Scalability: Whether you’re working with a single monitor or a six-monitor setup, SmartWindows grows with you.
Cross-Platform Potential: Although currently optimized for Windows, future updates could expand SmartWindows to other platforms, making it even more versatile.

SmartWindows
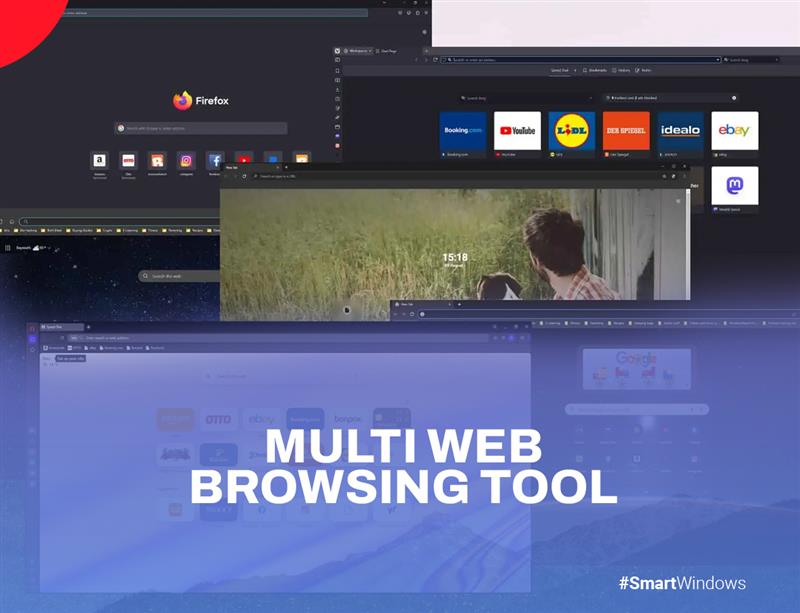
Restore Browser Tabs with SmartWindows. It maintains an active tab history and restores browser size as well as display position on one screen or many.
Conclusion:
SmartWindows represents the next generation of window management. Its innovative features, such as Custom Hotkeys, Scene Restoration, SmartText, and Instant Profile Sharing, make it a powerful tool that can supercharge productivity across industries. While DisplayFusion offers basic multi-monitor support, it lacks the smart automation, comprehensive app integrations, and forward-looking design that SmartWindows provides.
The difference is clear: SmartWindows is designed for a smarter, more efficient 2025—with automation, customization, and advanced integrations that make it the perfect choice for professionals looking to optimize their workflows.
Don’t let outdated systems hold you back—transform your workflow with cutting-edge automation and multi-monitor support.
For a more efficient, smarter 2025, SmartWindows is the clear choice. Take control of your workspace today with SmartWindows and experience productivity like never before.
So, here is the the all information you’re looking for about SmartWindows vs DisplayFusion.